

The serotonin reuptake system in the ENS is also inhibited by selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. As in the central nervous system, a serotonin reuptake system is present in the enteric nervous system (ENS). However, the role of 5-HT in the control of gastric motility can be investigated in an alternative way.
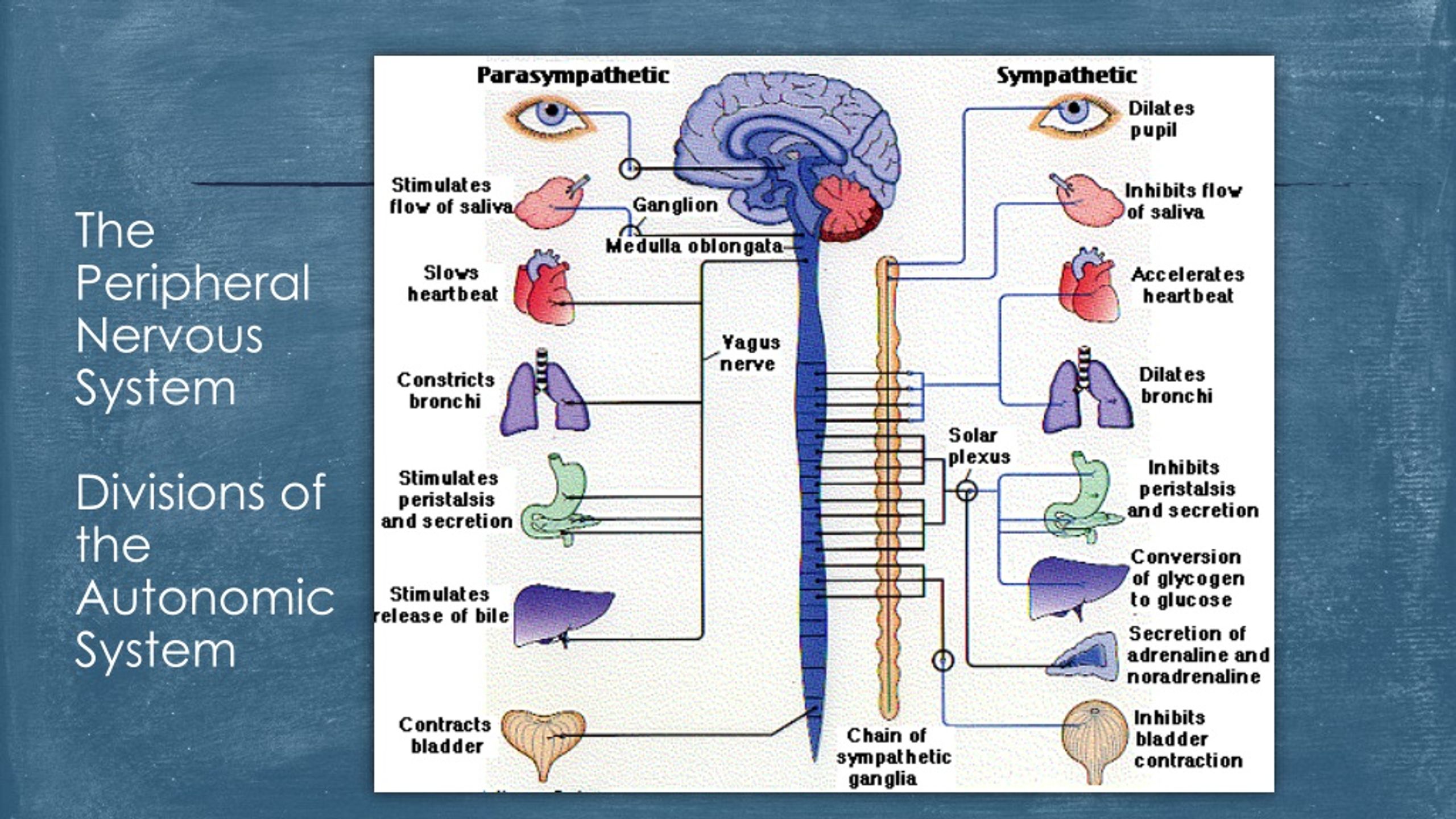
The lack of suitable selective 5-HT ligands for in vivo use in humans hampers the investigation of this issue. In humans, it is unknown whether the accommodation reflex also involves serotonergic activation of nitrergic neurons. More recently, it was demonstrated that 5-HT-induced relaxation of the guinea pig stomach is mediated via the release of nitric oxide through activation of a 5-HT 1-like receptor. In the mouse and in the guinea pig, involvement of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) receptors on intrinsic neurons in vagally mediated gastric relaxation has been demonstrated. Subsequently, the meal is emptied from the stomach at a rate that matches the absorbtive capacity of the duodenum. The accommodation reflex consists of relaxation of the proximal stomach, providing the meal with a reservoir and enabling a volume increase without a rise in pressure. Schematic illustration of the role of accommodation to a meal. 27 In a study in healthy volunteers, pretreatment with l-NMMA dose dependently decreased the gastric accommodation to a meal, thereby establishing that the gastric accommodation reflex in humans involves activation of nitrergic neurons.įIGURE 1. 25,26 These properties were used to test the hypothesis that NO is involved in the control of postprandial gastric tone in humans. Studies using this agent have been able to demonstrate the involvement of NO in the control of interdigestive motility and in mediating transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxations in humans. N G-monomethyl- l-arginine ( l-NMMA) is an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase (NOS), suitable for use in humans. 18,19 Several lines of evidence suggest a role for nitric oxide (NO) and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide as inhibitory neurotransmitters mediating gastric relaxation. Studies in animals have demonstrated that the gastric accommodation reflex is mediated via a vagovagal reflex pathway that activates non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic neurons in the gastric wall. Jan Tack, in Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract (Fifth Edition), 2012 34.4.2 Role of Nitrergic Neurons Supranuclear control of the accommodation reflex comes from widely distributed areas, which include the supraoculomotor area (which lies within the mesencephalic reticular formation just dorsal to the oculomotor complex) and numerous cerebral and cerebellar eye movement command centers. Innervation of the accommodation reflex is derived from the visceral nuclei of cranial nerve III, most notably the Edinger-Westphal nucleus. During near accommodation, the ciliary bodies contract (i.e., shorten), which relaxes the zonule and rounds the lens (i.e., thickens it).

During far vision, the ciliary bodies relax, the zonule stretch, and the lens flattens. Accommodation for near objects occurs from relaxation of the zonule. The ciliary bodies anchor suspensory ligaments, collectively called zonule, which stretch the lens and alter its refractive power. The accommodation reflex (or near response) is a three-part reflex that brings near objects into focus through lens thickening, pupillary constriction, and inward rotation of the eyes-eye convergence. Adam Fisch, in Nerves and Nerve Injuries, 2015 Accommodation for Near Vision


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
